We are studying the semantic indexing method for associating other texts semantically similar and recommending them as an example to the arbitrary sites of the text read and written by a user in this project. Moreover, our subjects include paraphrasing, error correction, and template extraction for sentence generation, with the aim of developing a practical application that assists paper writing in English for non-native speakers.
Building a Writing Assistance System Based on Communicative Functions of
Formulaic Expressions for Scholarly Papers
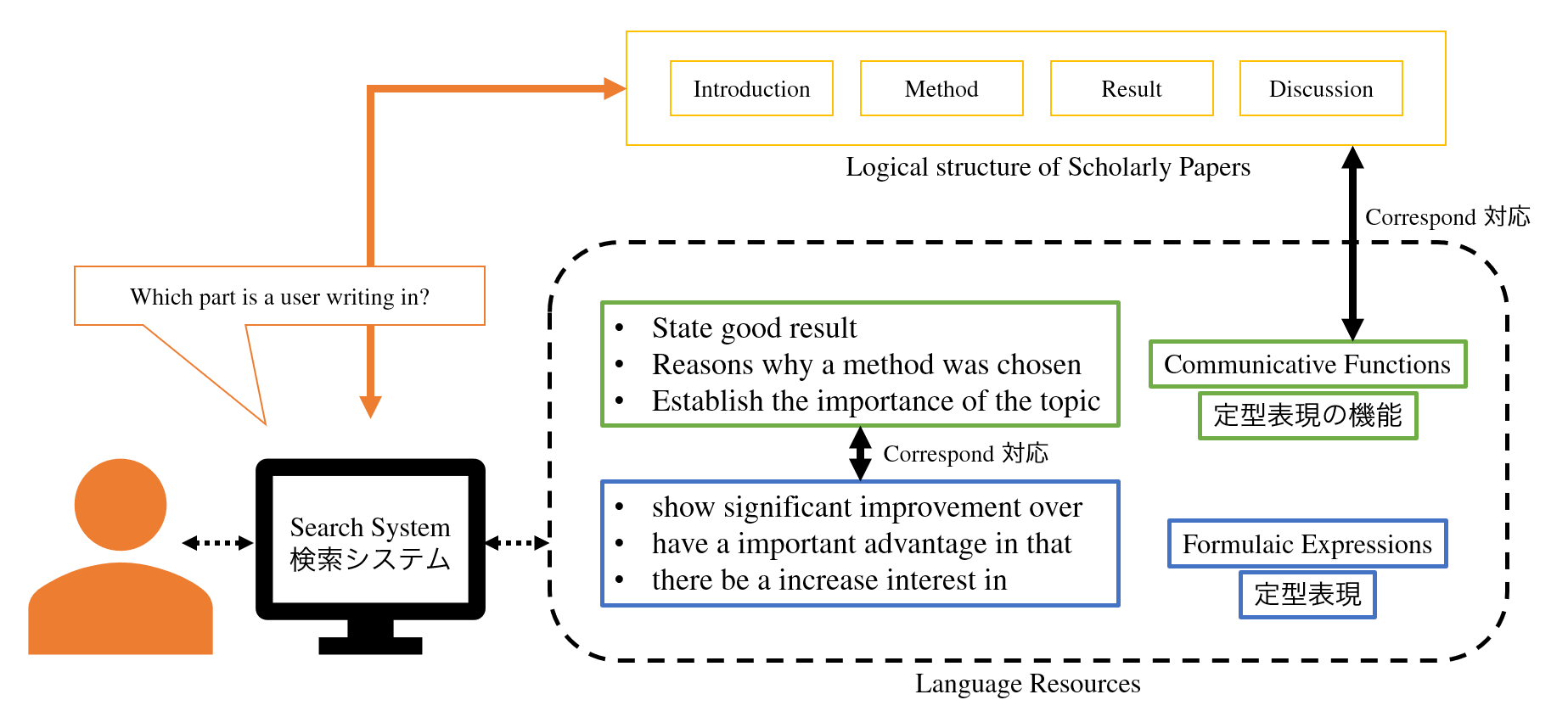
Formulaic expressions have been found to be helpful in writing scholarly papers, but it is costly to search for desirable formulaic expressions because there are few digitalised resources and existing retrieval systems are not efficient enough to save labour. Key-word-based searching, which most existing systems adopt, does not provide users with a wide variety of formulaic expressions. To alleviate this problem, we proposed a new scheme of formulaic expression retrieval that utilises communicative functions of formulaic expressions (Iwatsuki & Aizawa, COLING 2018
[link]).
It is widely known that the usage of formulaic expressions and communicative functions differs across disciplines, which raises the need for domain-specific databases of formulaic expressions labelled with communicative functions.
In order for efficiently constructing such domain-specific databases, we are developing a method for automatically annotating formulaic expressions with communicative functions (Iwatsuki et al., LREC 2020 [link]). Additionally, we also developed an evaluation dataset for the formulaic expression extraction, which had been evaluated by hand before (FECFeval [link]).
Distributed representation for similar sentence search
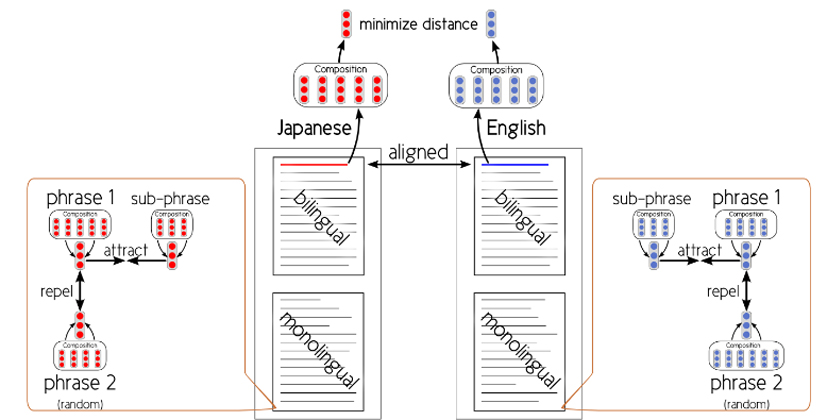
We propose a neural network that learns the semantic expression of phrases based on a novel standard called Inclusion criterion, which has implemented a multilanguage similar sentence search function. Furthermore, we have applied the proposed method to a Japanese–English bilingual corpus extracted from papers, and prepared a demonstration tool for English composition support CroVeWA. (Hubert et al.: NAACL HLT 2015 demo [link], ICLR 2015 short [link])